Principle of Operation
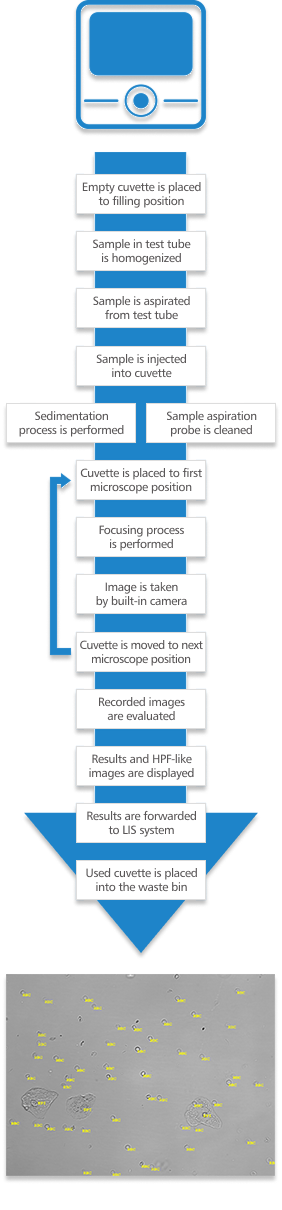
The operation theory is based on traditional manual microscopy, which is made automatic and operator independent. The instrument processes native urine samples, which are homogenized and filled into a cuvette. After sedimentation, the cuvette is moved to the microscope table, where a built-in camera captures digital images. Automatic focusing at all positions ensures well-focused images of each field of view, followed by the disposal of the used cuvette.
These images are analyzed by a real-time image processing software, the Artificial Intelligence-based Evaluation Module (AIEM).
The detailed measurement sequence is shown in the chart on the right. For more details, click on each step.
The detailed measurement sequence is shown in the chart on the right. For more details, click on each step.
AIEM Capabilities
The AIEM software automatically classifies and counts various urine sediment particles, including:
- Red Blood Cells (RBC)
- White Blood Cells (WBC)
- White Blood Cell Clumps (WBCc)
- Squamous Epithelial Cells (EPI)
- Non-squamous Epithelial Cells (NEC)
- Hyaline Casts (HYA)
- Pathological Casts (PAT)
- Bacteria (BAC)
- Rod and Cocci bacteria (BACc and BACr)
- Crystals (CRY)
- Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate (CaOxd), Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate (CaOxm), Triple Phosphate (TRI), Uric Acid (URI)
- Yeast (YEA)
- Mucus (MUC)
- Spermatozoon (SPRM)
- Amourphous (AMO)
AIEM flags samples for the suspected presence of:
- Acanthocytes (RBCa)
- Ghost Red Blood Cells (RBCg)
The images provide detailed views of all other sediment particles as well, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and enabling the user to see the morphology of each and every particle. The instrument also supports educational and research purposes by allowing manual identification of rare sediment particles.
Additional Capabilities
Other visible particles include:
- Red Blood Cell subclasses
- Renal and Superficial/Deep Transitional Epithelial Cells
- Pathological Cast subtypes
- Additional Crystal subtypes (Calcium Phosphate, Cystine, Leucine, etc…)
- Lipids
- Parasites (Schistosoma Haematobium, Enterobius Vermicularis, Trichomonas Vaginalis, Balantidium Coli, etc…)
Proven Efficiency
The instrument's efficiency and diagnostic performance have been validated by various studies. For further details, please visit the Literature tab on our website.
Body fluid mode
Certain members of the instrument line are capable of the investigation of body fluid samples. The instrument is capable of the investigation of cerebrospinal, pleural, ascites, pericardial, continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and synovial fluid samples. The investigation of WBC nuclei is an important part of body fluid analysis. In order to be able to do that properly a special liquid cell dye is available for the users of the instrument.
In body fluid mode the instrument detects the following parameters:
- White Blood Cells (WBC)
- Red Blood Cells (RBC)
- White Blood Cell differential count:
- Mononuclear White Blood Cells ratio (MN)
- Polymorphonuclear White Blood Cells ratio (PMN)
- Other Nucleated Cells (ONC)
AIEM flags body fluid samples for the suspected presence of:
- Bacteria (BAC)
- White Blood Cell Clumps (WBCc)